HTMLifier Mac OS
HTMLifier Mac OS
OpenWYSIWYG is an open-source WYSIWYG HTML editor for macOS 10.15 with affluent text editing attribute. Some of its attractive characteristics include open source licensing, sleek user-interface, and powerful editing environment. It sounds like you may not be using the default apache for os x. – Camden Narzt Sep 23 '14 at 3:30. Have you restarted the server? Apachectl restart – makepkgnotwar Mar 29 '15 at 5:13. Problem accessing localhost on Mac OS X Mavericksit was working fine until I rebooted today. Virtual Hosts Not Working on OSX Mavericks. The Scratch project format (.sb, sb2, or.sb3) can only be read by the Scratch editor. Compiling a scratch project can convert it to another format that can be opened without Scratch. Compiling was a popular suggestion for Scratch 2.0, However, it wasn't added in the normal online or offline editors. To get around this, many Scratchers have made ways to turn Scratch Projects into more widely. HTML-Kit has always been a native Windows application but I get many requests for a native Mac version. Unfortunately, there's no magical switch for converting a complex Windows app to a Mac app. Besides, I think software works best when they're designed from ground up for specific platforms. Download Mac software in the HTML Tools category. Native macOS Gmail client that uses Google's API in order to provide you with the Gmail features you know and love, all in an efficient Swift-based app.
(An HTML file that can be opened and used in the browser without an internet connection)
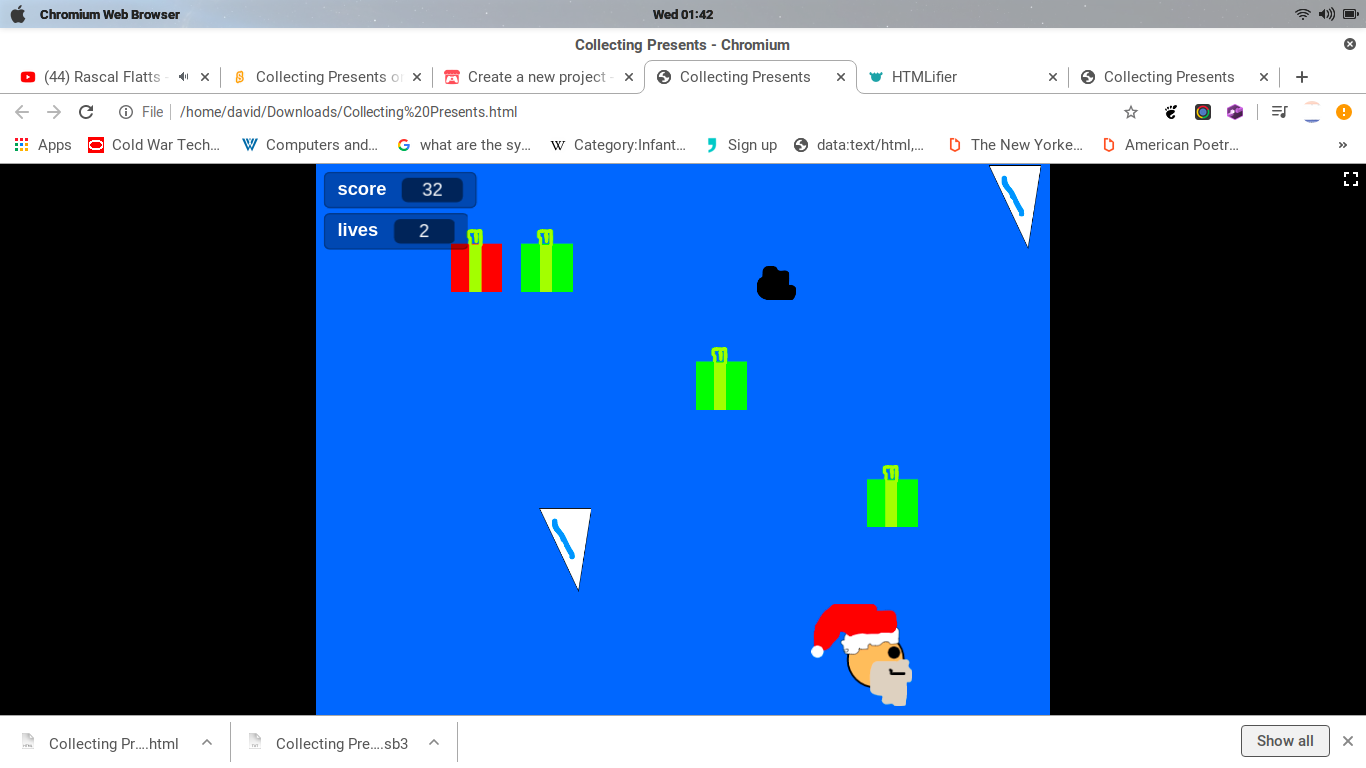
This packages your Scratch project into a single HTML file that can run on its own in a web browser. The HTML file will be pretty big because it contains the entire Scratch engine (2.6 MB) and the costume and sound files used in the project.
The HTMLifier may not be the best option for you; refer to the See also section for alternatives.
The project will automatically start, and there are no green flag or stop sign buttons.
Save options in link · HTMLify
If you want to view or edit the HTML file, you can use the specialized Large File Editor to hide the long lines that may hang or crash normal text editors.
Update history
See the code and previous versions on Github.
2021-03-16 (download)
- New cloud behaviours:
☁ urlcontains the current URL of the web page.☁ pastedcontains the last pasted text by the user.☁ username, when set, will change what the 'username' block reports.
- Fixed the background image not showing in full screen.
- Fixed the progress bar being shown under the loading image.
2021-02-07 (download)
- Save the options in the URL
- New customisation options:
- Background image
- Cursor
- Favicon
- New loading bar design with customisable colours
- Loading screen image from a URL
- Option to stretch only the loading screen image
- Option to show start/stop buttons (equivalent to the green flag/stop sign)
- New special cloud behaviours:
- Better support for
☁ evalreturning Promises ☁ open linkopens a URL in a new tab.☁ redirectredirects to a URL.☁ set clipboardtries to copy text to the clipboard.☁ set server ipchanges the cloud server URL.
- Better support for
- Ability to distinguish between left/right modifier keys using
<key (join [code_ShiftLeft] []) pressed?>>, for example. - Clicking on a variable slider no longer gives it focus, so keys will continue to work.
- A bookmarklet creator
- BREAKING: The mouse lock position now sets mouse x/y to the accumulative mouse position, which should be more reliable. This works best with the 'Remove limits' option.
- Updated CSS by Mr. Cringe Kid
- Fixed the HTMLification log progress not resetting
- Also, the primitive cloud server has been updated.
2020-12-18
- Specific mouse buttons can now be detected using
<key (join [MouseN] []) pressed?>, whereNcan be 1 for left click, 2 for middle click, 3 for right click, and 0 for touch/pen. - Fixed an issue where Scratch 2.0 projects with bitmap costumes wouldn't work.
2020-06-13 (download)
- More options for styling variable/list monitors
- Option to generate a .zip of files
- Option to preview the HTMLified project
- Readded the option for a progress counter despite lack of demand
- Warn if a file might be too large for JavaScript to HTMLify
- Fixed HTMLifying 2.0 projects

2020-06-01 (download)
- Option to remove clone/list length limits
- Option to hide the cursor
- Ability to distinguish between cloud variables for localStorage and the server (and run JavaScript using cloud variables)
- Option for rudimentary pointer lock
- Fixed mouse position and unresized lists not showing
- Default project changed to one of ScratchCat's
- Unfortunately, as part of these changes, I removed the option for a progress bar. If there's demand, I'll try to add it back.
2020-05-01
- Support for custom extensions from a URL
- CSS by Mr. Cringe Kid
2020-03-29 (download)
- Fixed custom stage sizes
2020-03-27
- Show an image such as a gif while loading
- Fixed dragging sprites simulating another green flag click
2020-01-06
- An offline version of the HTMLifier
2019-12-25
- An option to use a custom cloud server for cloud variables instead of saving to localStorage
2019-11-23
- A fullscreen button
- An option to change monitor colours
2019-10-05
- New ask box
2019-09-28
- A status text that shows the assets loaded
- Support the video extension
- Support draggable sprites
2019-08-08
Htmlifier Mac Os Catalina
- Removed 'Scratch' from the name of this utility just in case
2019-07-27
- Support 16:9 projects
- Simplify the number of modes for HTMLification
2019-07-13
- Cloud variables store in localStorage
2019-06-29
- Upload project file instead of using project ID
- Toggle compatibility and turbo mode
2019-03-31
- Variable and list watchers
2019-02-09
- Project start
Credits
Made by Sheep_maker, who used scratch-vm, download.js, JSZip, and their dependencies for this project.
CSS by Mr. Cringe Kid.
See also
Depending on your use case, the HTMLifier may not be the best option for you. The HTMLifier prioritizes accuracy by using almost the same engine that vanilla Scratch uses, sacrificing speed and editability.
Scratch to JavaScript compilers (best for performance): Phosphorus (Scratch 2.0), Forkphorus, and TurboWarp.
Scratch to JavaScript converter (best for learning JavaScript): Leopard
Use the offline application cache to store HTML, JavaScript, CSS, and media resources locally, to create web-based applications that work even when a returning user is not connected to the Internet. You can also use the offline application cache simply to store static resources locally, to speed access to your website and lessen the server load when a user returns to your site.
The offline application cache lets you create web apps—such as canvas-based games, e-readers, and JavaScript calculators—that people can return to your site and continue to use even when they have no internet connection.
To use the offline application cache, you must create and declare a manifest file. The manifest file is a text file that contains a list of resources to be cached. Declare the manifest file in your HTML using the manifest attribute:
<html manifest='path/filename'>
When a user comes to your website for the first time, Safari loads the webpage that declares the manifest—along with all the resources listed in the manifest file—from the web and stores copies in a cache. On subsequent visits, the webpage and resources are loaded directly from the cache, whether the user is online or offline. If the user is online, and the manifest has changed since the user’s last visit, a new cache is created and used on the following visit. (You can reload the site from the new cache immediately using JavaScript.)
Important: You must modify the manifest file to trigger a cache update. Changing the HTML file that declares the manifest has no effect on users returning to your site unless you change the manifest file as well. If the manifest file is unchanged, the HTML file that declares the manifest is loaded directly from the cache.
When you specify a manifest file, you are telling Safari that your website is designed to operate offline. Consequently, Safari does not attempt to access resources unless they are listed in the manifest and stored in the cache. If you need to access online resources for your website to work correctly, specify the URLs or URL patterns in the NETWORK section of the manifest, as described in Creating a Manifest File.
If your website consists of multiple HTML pages that should all be cached in order for your site to operate correctly, list all of the pages in the cache manifest, and include the manifest attribute in every one of the HTML pages.
If you are using the offline application cache to speed access to your site for return visitors, instead of using the cache so your site can be used when the user is offline, be sure to specify your network URL pattern as *, so that all network access is enabled, and remember to update the manifest file whenever you update your site.
Creating a Manifest File
The manifest file specifies the resources to download and store in the application cache. Resources can include HTML, JavaScript, CSS, and image files. In Safari 5.1 and later, the manifest can specify audio and video media files as well. After the first time a webpage is loaded, the resources specified in the manifest file are loaded directly from the application cache, not from the web server.
The manifest file has the following requirements:
The file must be served with a MIME type of
text/cache-manifest. For most web servers, the filename must end in.manifest.The file must have the same origin (domain and scheme) as the HTML file that declares it.
The first line of the file must consist of the text
CACHE MANIFEST.Subsequent lines may contain section headings, URLs of resources to cache, network URLs, or comments.
Section headings consist of a single word, followed by a colon. Legal values are
CACHE:,NETWORK:, orFALLBACK:.Resource URLs can be absolute or relative to the manifest file (not necessarily relative to the HTML page that uses the resource).
Network URLs may contain an asterisk as a wildcard character.
Comments must be on a single line and preceded by the
#character. Comments may appear in any section of the manifest.
The manifest has one or more sections. There is normally a CACHE section, followed by an optional NETWORK section. There may also be FALLBACK sections and additional CACHE sections.
The CACHE Section
A CACHE section consists of a list of URLs of resources to be cached. By default, the manifest begins with a CACHE section declared implicitly. For example, your manifest may consist of the CACHE MANIFEST heading followed by a list of resource URLs, with no section heading.
If your manifest has other section types, followed by a CACHE section, however, you must declare any subsequent CACHE section explicitly using the CACHE: section header.
The CACHE sections of your manifest should list the URL of every resource your website needs to operate correctly when the user is offline. Resource URLs can be absolute or relative to the manifest file. Each URL must appear on a separate line.
You do not need to include the URL of the HTML file in which the manifest is declared; that file is included in the cache automatically.
The NETWORK Section
If your website requires online resources to operate correctly, you must declare the URLs of the resources in the optional NETWORK section of the manifest file. These URLs comprise a whitelist of resources to access using the network.
Important: Resources that are not in the cache, and are not included in the whitelist, are not loaded.
A NETWORK section begins with the section header NETWORK: on a line by itself. This is followed by a list of URLs or URL patterns, each on its own line.
A URL may be a complete file specifier or a prefix. If the URL is a prefix, all files sharing the prefix are on the whitelist. The asterisk character (*) may be used as a wildcard that matches all URLs. For example:
http://example.com/myDirectory/myFile.jpgputsmyFile.jpgon the whitelist.http://example.com/myDirectory/puts all files inmyDirectoryon the whitelist.http://example.com/puts all files inexample.comon the whitelist.*puts all files on the Internet on the whitelist.
Fallback Sections
A manifest can contain optional FALLBACK sections. A FALLBACK section contains one or more pairs of URLs. The first URL in each pair is the preferred URL for a resource to be cached. The second URL in the pair is a fallback URL to use if the file is inaccessible using the first URL.
A FALLBACK section begins with the section header FALLBACK: on a line of its own. Each URL pair appears on a separate line, with the two URLs separated by a space. For example:
FALLBACK:
http://example.com/myFile http://server2.example.com/myFile
../media/image2.jpg ../legacy/genericImage.jpg
The example just given caches myFile from example.com, falling back to an alternate server in the same domain if the file is inaccessible using the first server. The example then caches an image from the media directory, falling back to a generic image in the legacy directory if the preferred image is unavailable.
Important: All FALLBACK URLs must have the same origin as the manifest file. That is, they must be in the same domain and use the same access scheme.
The fallback section can also be used to add pages from your site to the cache “lazily,” as the user loads them. Such use of the fallback section allows the user to revisit previously opened pages while offline, but specifies a default page to use when an offline visitor attempts to open a new page. For example:
FALLBACK:
/ /myDirectory/notAvailable.html
In the example just given, the URL pattern “/” matches all files with the same origin as the manifest file—all the pages on your site. Any page from within your domain is therefore added to the cache when the user loads it and remains available when the user is offline. If the user attempts to load a new page while offline, the file notAvailable.html is used instead.
For lazy caching to work, each page to be cached must include the manifest attribute in the <html> tag.
Example Manifest File
A sample manifest file is shown in Listing 1-1.
Listing 1-1 Sample manifest file
Updating the Cache
When Safari revisits your site, the site is loaded from the cache. If the cache manifest has changed, Safari checks the HTML file that declares the cache, as well as each resource listed in the manifest, to see if any of them has changed.
A file is considered unchanged if it is byte-for-byte identical to the previous version; changing the modification date of a file does not trigger an update. You must change the contents of the file. (Changing a comment is sufficient.)
Tip: It’s good practice to include a version number in a comment line of your manifest file. Whenever you update the resources your website uses, update the version number in the manifest file as well.
If the manifest file has changed, and checking reveals that a resource file has changed, the new version is copied into the cache.The newly cached resources are not immediately used, however, as that would result in reloading changed resources piecemeal as they are cached. Instead, all of the changed resources are loaded as a group the next time the user revisits your site.
In other words, users who return to your site do not see changes immediately. They see changes when they return a second time. If you want Safari to reload the site with the changed resources the first time a user returns to your site, you can trigger an update using JavaScript.
To interact with the application cache from JavaScript, work with the applicationCache object. To force a reload of the contents of the new cache, respond to an 'updateready' event whose target is the cache by calling the cache’s swapCache() method, as shown in the following snippet:
The 'updateready' event fires when all of the changed resources have been copied into a new cache. Calling swapCache() loads the new cache, causing your webpage to reload,
Note that errors can occur when updating the application cache. A resource may be inaccessible, for example, or the manifest file may be modified in the midst of a cache reload. If a failure occurs while downloading the manifest file, its parent HTML file, or a resource specified in the manifest file, the entire update process fails. The browser continues to use the existing version of the application cache and the 'updateready' event does not fire. If the update is successful, Safari uses the new cache the next time the site is loaded.
Note: Using JavaScript to add and remove resources from the application cache is not supported.
See the documentation for DOMApplicationCache for a complete list of application cache event types.
Debugging Offline Applications
Debug offline applications using Safari’s built-in developer tools. Enable the developer tools in Safari preferences, open your webpage in Safari, and choose Show Web Inspector from the Develop menu.
Click the Resources button in the Web Inspector to inspect the application cache. The display of cached data is not updated dynamically as the cache is modified; to refresh the display, click the “recycle” button in the bottom bar.
For more information about using the Web Inspector, see Safari Web Inspector Guide.
Testing Files Locally
You cannot test offline applications by dragging a local webpage into Safari. Safari uses the manifest file only when it is loaded with the MIME type of text/cache-manifest, which requires loading the manifest from a web server.
Important: The manifest filename should end in .manifest.
If you are developing on Mac OS X, your Mac has a built-in web server that you can use to test your manifest file locally. Enable web sharing in System Preferences and drag the website into your Sites directory, then type the IP address of the local web server into Safari’s address bar. The site should open, and the manifest file and all the listed resources should load into the application cache and be viewable using the Web Inspector.
To verify the behavior of your website when the user is offline, turn off web sharing in System Preferences and reload your website in Safari. The site should open normally using the cached files.
Testing Offline Applications Remotely
To test an offline application website installed on a remote server, load the site normally, then take Safari offline and load the site again.
Safari operates in offline mode only when there is no Internet connection. To test your web-based application in offline mode, disconnect the device you wish to test from the Internet. For example, put an iOS-based device into Airplane Mode, or create and choose a nonfunctioning network connection in Mac OS X System Preferences.
Tip: On iOS-based devices, you can add your offline application website to the home screen to make reloading your site easier.
Monitoring and Logging Cache Events
When debugging offline applications, it can be helpful to monitor and log cache events. The applicationCache element generates the following events:
'checking'—Safari is reading the manifest file for the first time or checking to see if it has changed. This event should always fire once.'noupdate'—The manifest file has not changed.'downloading'—Safari is downloading a changed resource.'cached'—Safari has downloaded all listed resources into the cache.'updateready'—A new copy of the cache is ready to be swapped in.'obsolete'—The manifest file is code 404 or code 410; the application cache for the site has been deleted.'error'—An error occurred when loading the manifest, its parent page, or a listed resource, or the manifest file changed while the update was running. The cache update has been aborted.
The snippet in Listing 1-2 can be added to the <head> section of your webpage to monitor and log the cache events. For more information about logging using the console API, see Safari Web Inspector Guide.
Listing 1-2 Log cache events
Htmlifier Mac Os Download
Htmlifier Mac Os 11
Htmlifier Mac Os X
Copyright © 2011 Apple Inc. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Policy Updated: 2011-09-21
HTMLifier Mac OS
